“Today’s Russian Plane Crash: A Nation Mourns as Soviet-Era Aircraft Falls Again” On July 24, 2025, tragedy struck in Russia’s far-east when an Antonov An‑24 turboprop passenger plane, operating under Angara Airlines, crashed near Tynda in the Amur region, killing all aboard. The disaster has brought fresh sorrow to countless families—and reignited urgent debates about the nation’s aging aviation fleet.
The Flight and the Disaster
At approximately 1:05 p.m. local time, the An‑24, built in 1976, was on approach to land at Tynda Airport, coming from Khabarovsk via Blagoveshchensk—both cities near the China–Russia border. On its second landing attempt, after failing to touch down the first time, it vanished from radar. Shortly thereafter, a search helicopter detected a burning fuselage nestled amid dense, hilly woodland about 15 km (9 miles) south of Tynda.
“Today’s Russian Plane Crash: A Nation Mourns as Soviet-Era Aircraft Falls Again” Emergency services, halted by rough terrain, used heavy equipment and on-foot rescue efforts to locate the wreckage. Russian officials confirmed 48 fatalities, including 42 passengers (five of whom were children) and six crew members. Initial confusion over the numbers saw some outlets report as many as 49 or 50 aboard.
President Vladimir Putin expressed deep condolences and opened a formal criminal investigation into “flight safety rule violations leading to multiple deaths”. The Amur region governor, Vasily Orlov, has declared a three-day mourning period.
A Passenger List: Who Were They?
While a complete passenger manifest remains pending release, early reports and informal accounts suggest a mix of families, professionals, and travelers:
- Among the passengers were five children—a heartbreaking reminder of lives cut tragically short.
- The co-pilot, Kirill Plaksin (37)—scheduled to appear in court that very day for alleged refusal to undergo a narcotics test—perished alongside 61-year-old Captain Vyacheslav Logvinov.
- Reports mention a grieving flight attendant, medical professionals, and a school teacher, underscoring the tragedy’ s reach across ordinary lives and professions.
One survivor anecdote—though not confirmed—tells of a woman who missed the flight to care for her ill granddaughter. Such stories reflect the heartbreaking fate of those who boarded—and the relief of those who didn’t.
Under the Lens: Aircraft History & Safety Concerns
“Today’s Russian Plane Crash: A Nation Mourns as Soviet-Era Aircraft Falls Again” The flight’s aircraft—a 1976 Antonov An‑24—was nearly 50 years old, earning the nickname “flying tractor” for its ruggedness. In use for decades in Russia’s remote regions due to its ability to operate in harsh weather with minimal infrastructure, it nonetheless raises mounting concerns.
Before the crash, Angara Airlines operated 10 similar An‑24s, all aged between 1972 and 1976. These aircraft have been involved in 88 fatal crashes and 65 severe incidents over their lifespans; only about 75 remain active.
Since 2018, the crashed plane reportedly underwent four “minor incidents,” yet had recently passed a technical safety inspection. But with Western sanctions limiting access to spare parts and infrastructure, maintaining such vintage aircraft has become increasingly precarious.
What We Know—and Don’t—About the Crash
Immediately after the crash, officials highlighted several key facts:
- The aircraft was attempting a second landing amid poor weather conditions, including low clouds and heavy rain.
- There was no distress signal, and air traffic control lost contact without warning.
- Some early analysis suggests crew error during a complex approach may have played a role, although weather and possible technical issues are still being examined.
A criminal probe is already underway, as mandated in cases involving multiple fatalities. Investigators from the Far Eastern Transport Prosecutor’s Office and the Interstate Aviation Committee (MAK) are combing through flight logs, maintenance records, crew credentials—and, when recovered, the black boxes.
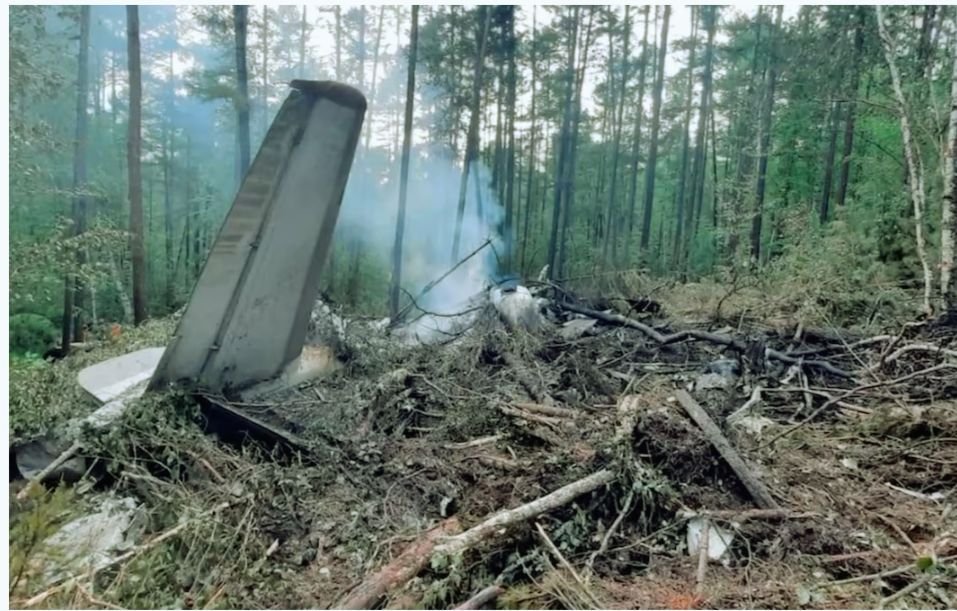

Rescue & Recovery: Battling Terrain to Bring Closure
“Today’s Russian Plane Crash: A Nation Mourns as Soviet-Era Aircraft Falls Again” Search teams faced immense obstacles due to the isolated, forested landscape of the crash site.
With no direct road access, rescue teams were forced to hike in and bring heavy machinery to clear paths. The terrain, dense with firs and birch, complicated operations, while fire from the wreckage further hindered efforts.
Russian officials deployed 149 specialists and 21 units to aid in search, recovery, and salvage efforts. Emergency responders identified bodies and personal belongings to begin the heartbreaking process of notifying families and launching DNA identification procedures.
Russia’s Aging Aviation System: A Broader Crisis
This is not Russia’s first aviation disaster—and likely won’t be its last.
Since 2018, several fatal accidents have involved Soviet-era aircraft in Russia’s remote regions. The problem—overreliance on aging aircraft, coupled with sanctions restricting access to modern parts and systems—is now at a tipping point.
Experts argue that although the An‑24 is durable and straightforward to maintain, its safety record is alarmingly poor. A fatal 2011 Siberian crash prompted then-President Dmitry Medvedev to recommend retiring the aircraft fleet.
Now, with dozens of these vintage workhorses still flying over far-flung landscapes, the crash is intensifying calls for fleet renewal: replacing old An‑24s with modern regional turboprops or jets, and strengthening pilot training programs, air traffic control systems, and maintenance protocols.

National Grief and International Repercussions
Upon news of the crash, Russia mourned deeply:
- A minute’s silence was held at the outset of a government meeting following condolences from President Putin.
- The Amur region’s three-day mourning period, led by Governor Orlov, reflects regional grief.
- Overwhelmed families have found limited closure, with some receiving news through brief media bulletins.
Beyond Russia, there is international attention:
- China, near the crash site, sent condolences—reportedly including at least one Chinese citizen among the victims.
- Other nations still operating An‑24s—North Korea, Kazakhstan, Cuba, Ethiopia, Myanmar, Zimbabwe—may now assess their own fleets carefully.
- International bodies like IATA and ICAO are expected to support Russia’s review of its safety practices.
Personal Narratives: Lives Cut Short
While investigation details unfold, the human dimension must not be forgotten:
- Five children boarded the flight—faces bright with future hopes, their stories gone in an instant.
- Crew members like co-pilot Kirill Plaksin and Captain Logvinov, both experienced, died fulfilling their duties.
- Families recount final calls, unread messages, and unplanned changes—such as the woman grounded by her granddaughter’s illness.
Tragedies like this leave enduring voids: a child’s birthday absent a parent, a bride missing her husband, a community without beloved teachers or doctors.

Investigation & Questions Ahead
Key areas under investigation:
- Weather conditions: Was heavy rain/clouds to blame?
- Crew actions: Did pilot error occur during the second approach?
- Technical issues: Any engine malfunctions or avionics failure?
- Aging aircraft risks: Did the plane’s vintage systems play a role in the emergency?
The black boxes, once recovered and decoded, could offer crucial insights into cockpit communications, system performance, and timeline before the crash.
Safety Overhaul: What Must Change
To prevent future disasters, Russia must consider:
- Retiring old An‑24s and procuring newer aircraft types.
- Bolstering maintenance, including access to Western-equivalent parts despite sanctions.
- Enhanced pilot training, especially for challenging landings under adverse weather.
- Upgrading ATC, radar, and approach aids at remote airports like Tynda.
- Stronger regulatory enforcement, with greater oversight over regional carriers.
This accident may mark a turning point: a painful reminder that safety must outrank cost.
A Nation Reflects
In regions like Amur, flying is a necessity—roads are sparse, distances vast, winters harsh. But necessity should not excuse complacency. Every flight should honor a highest standard of safety.
This crash has reopened deep anxieties across Russia, especially among those using similar aircraft on short-haul routes. It’s triggered debates across state media, aviation forums, and social networks.
Conclusion: Tragedy with a Purpose?
The July 24, 2025 crash of the An‑24 near Tynda is more than a headline—it’s a moment of reckoning. With 48 lives lost, including children and professionals, this tragedy resonates far beyond remote Russian hills.
If this final tragedy catalyzes a long-overdue shift—a fleet modernization, safer skies, better-trained crews—perhaps then such loss might bear a meaning beyond sorrow. But only time—and decisive action—will tell.
For now, Russia grieves, world watches, and investigative teams labor through forest and metal to piece together the truth.
London Plane Crashhttps://blindspotnews.com/london-plane-crash-today/
Sole Survivor Miraculously Lives Through Air India Plane Crash in Ahmedabad That Kills 241https://blindspotnews.com/sole-survivor-miraculously-lives-through-air-india-plane-crash-in-ahmedabad-that-kills-241/








